6.1 Measuring Distance¶
The ultrasonic sensor module works on the principle of sonar and radar systems for determining the distance to an object.
Schematic
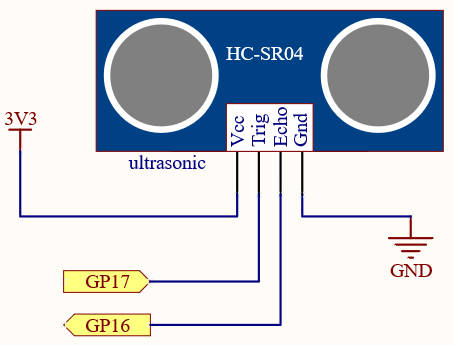
Wiring
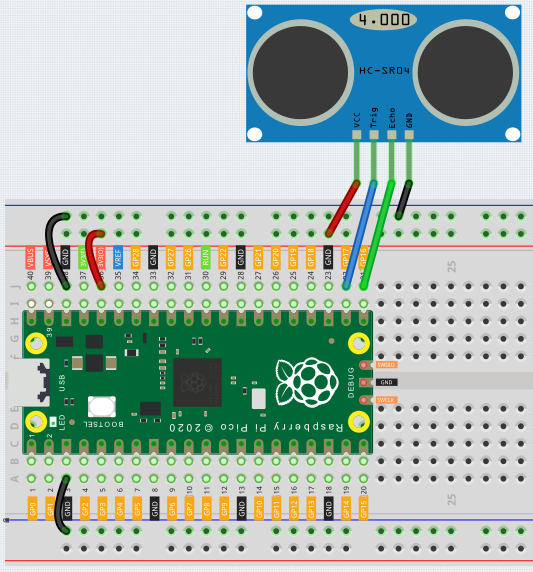
Code
Note
Open the
6.1_measuring_distance.pyfile under the path ofeuler-kit/micropythonor copy this code into Thonny, then click “Run Current Script” or simply press F5 to run it.Don’t forget to click on the “MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico)” interpreter in the bottom right corner.
For detailed tutorials, please refer to Open and Run Code Directly.
import machine
import time
TRIG = machine.Pin(17,machine.Pin.OUT)
ECHO = machine.Pin(16,machine.Pin.IN)
def distance():
TRIG.low()
time.sleep_us(2)
TRIG.high()
time.sleep_us(10)
TRIG.low()
while not ECHO.value():
pass
time1 = time.ticks_us()
while ECHO.value():
pass
time2 = time.ticks_us()
during = time.ticks_diff(time2,time1)
return during * 340 / 2 / 10000
while True:
dis = distance()
print ('Distance: %.2f' % dis)
time.sleep_ms(300)
Once the program is running, the Shell will print out the distance of the ultrasonic sensor from the obstacle ahead.
How it works?
Ultrasonic sensors produce high frequency sound waves (ultrasonic waves) emitted by the transmitting probe. When this ultrasonic wave hits an object, it is reflected as an echo, which is detected by the receiving probe. By calculating the time from transmission to reception, the distance can be calculated.
Based on this principle, the function distance() can be derived.
def distance():
TRIG.low()
time.sleep_us(2)
TRIG.high()
time.sleep_us(10)
TRIG.low()
while not ECHO.value():
pass
time1 = time.ticks_us()
while ECHO.value():
pass
time2 = time.ticks_us()
during = time.ticks_diff(time2,time1)
return during * 340 / 2 / 10000
Among them, the first few lines are used to transmit a 10us ultrasonic wave.
TRIG.low()
time.sleep_us(2)
TRIG.high()
time.sleep_us(10)
TRIG.low()
Then, the program is paused and the current time is recorded when the ultrasonic wave has been emitted.
while not ECHO.value():
pass
time1 = time.ticks_us()
Subsequently, the program is suspended again. After the echo is received, the current time is recorded once again.
while ECHO.value():
pass
time2 = time.ticks_us()
Finally, based on the time difference between the two recordings, the speed of sound (340m/s) is multiplied by the time to obtain double the distance between the ultrasonic module and the obstacle (i.e., one round trip of the ultrasonic waves from the module to the obstacle). Converting the units to centimeters gives us the return value we need.
during = time.ticks_diff(time2,time1)
return during * 340 / 2 / 10000
Note that the ultrasonic sensor will pause the program when it is working, which may cause some lagging when writing complex projects.